Foods are not only an energy source for our bodies. They contain important components that are vital for our metabolism and overall wellness. We may not realize, our immune system is one of the most vital organs of our body. And it’s fully powered by what we eat. So, a diet full of immune-supporting food is always necessary for your wellness journey. And with the help of some foods, you can enhance the maximum potential of your immunity, promoting overall well-being.
We are team My Organic Body & Diet. MyOrganicBD is a group of nutritionists, doctors, and microbiologists working together to create an in-depth scientific knowledge base about organic food & wellness. Reaching general people with greater knowledge is our top priority.
In this article, we will discuss the basics of the immune system diet & related things.
Let’s start.
What are the Basics of the Immune System and Food?
So, as we are diving into immune system-boosting food, let’s clear some easy concepts about the immune system. We have trillions of cells, billions of cell components, millions of tissues, and thousands of functions in our body. The combination or harmony of those consists of a regular function of our body. But our environment is full of disease-causing bacteria and viruses. They want to take over our bodies for the nutrients and multiply. A complex system is also prone to self-malfunction, like cancer or a tumor.
The defense system that protects our body from microorganisms, foreign bodies, and internal malfunction is our immune system. Now you should get the actual definition easily. A complex network of cells, tissues, organs, and the substances they make that help the body fight against infections and other diseases according to NCI.
Let’s discuss the components of the immune system in easy language without going too deep in the next sections.
What are the Key components of the Immune system?
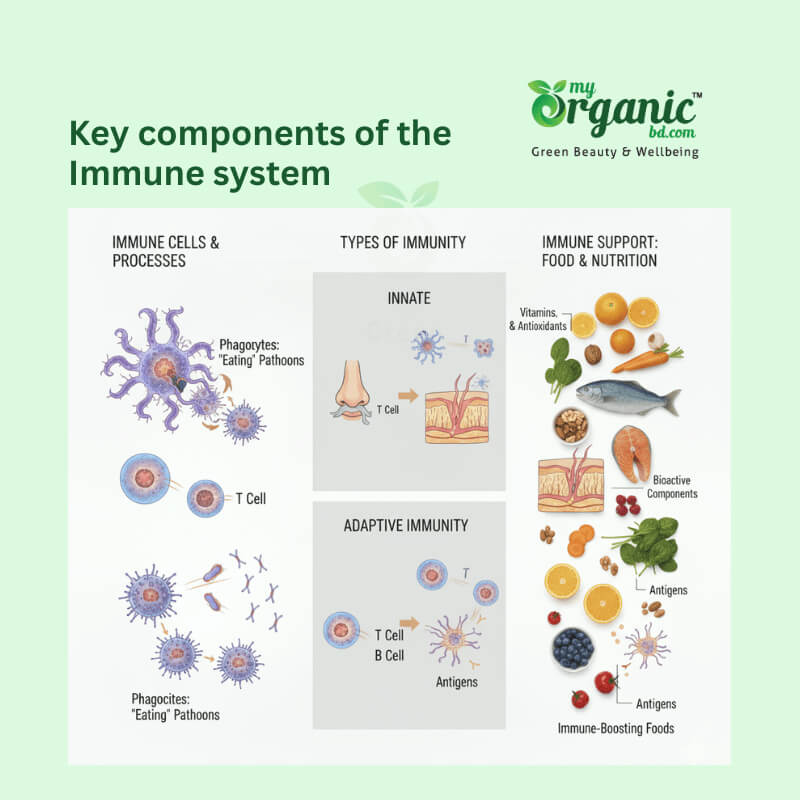
There are so many components and functions in the immune system. But the cellular defense is the core of our immunity. Immune cells are the specific cells that actively petrol our body and take care of anything foreign. It’s almost similar to the military. Different immune cells have different roles, and there are also ranks in some contexts. Take a look at the main cells and their respective roles.
White blood cells are the main soldiers of immunity. There are different types of WBC. Phagocytes eat pathogens like amoebae and destroy them. There are also T cells and B cells. Some T cells directly attack pathogens, and others attack cancerous cells. B cells mark the pathogen so other cells can follow the signal and destroy it. There are also memory cells. After killing a pathogen, its destroyed parts are not discarded immediately. They are memorized by the T and B memory cells. So, next time when the pathogen attacks, our body immediately remembers the pathogen and destroys it.
There is also some terminology you must remember. An antibody is a protein that is made by B cells to kill pathogens. And antigens are the foreign substance of a pathogen that triggers the immune response. There are 2 types of immunity. Innate immunity is fast and general, like phagocytes engulfing pathogens. Adaptive immunity is a slow and precise immunity. It is very accurate and provides stronger protection in the long term.
As you can see, a lot is going on in our bodies. And to function properly, our body needs proper amounts of vitamins. Minerals and antioxidants. Some bioactive components also improve certain functions of the immune system. With the basic knowledge of immunity, we can improve our knowledge further on immune-boosting food.
How does nutrition affect immune function and immune health?
Nutrients are the foundations of our immune system. They are both building blocks and maintenance agents of our immunity. Let’s discuss their role in the following part.
- Protein, folate, iron, vitamin B, and other micro and macronutrients are core ingredients of different immune cells like WBCs, B-cells, T-Cells, etc.
- Nutrients are required for the immune cells’ optimum function. They get energy from the nutrients, and also their proper function depends on the availability of nutrients. Nutrient deficiency slows down the immune cells.
- Vitamin A, zinc, and fatty acids nourish the skin and mucous membrane. Those are our bodies’ first line of defence. Different nutrients like Vitamin D, omega-3 fatty acids, and antioxidants help regulate the signaling of the immune system.
- Free radicals can damage the immune cells. Antioxidants like vitamin C, vitamin E, and selenium protect the cells from oxidative damage.
- About 70 percent of our immune system is active in our gut area. They maintain the gut bacteria, and also get training in killing the pathogens. So good gut health also results in better immunity. High fiber food, probiotics like yogurt and fermented food, and prebiotics like whole grains and vegetables are essential for better gut health.
Nutrients are also vital for the wellness of the organs that produce immune cells. Here is the short discussion on that.
- White blood cells and B cells are produced in the bone marrow. Iron, folate, and vitamin B12 are required for the synthesis. Protein works as the ingredient of those immune cells.
- Immune cells are trained in our thymus. Zinc and Vitamin A are the crucial components for the process.
- Immune cells are stored in the spleen and lymph nodes. Vitamin C, Vitamin D, and omega-3 are vital for the process.
- The majority of immune cells are active in our gut. Probiotics, prebiotics, Vitamin D, and zinc are essential for better gut health.
Please read Nutrients 101 – The Building Blocks of Organic Healthy Living to get a greater idea.
What are the core principles of an immune-support diet?
The first important thing to note is that a good diet itself does not improve the immune system. That means our immune system is already very complex and powerful. You can not supercharge the immunity. But a balanced diet is required to maintain its normal, effective state. With a proper diet, your immune cells will multiply as they should, they will function properly, and decrease your chance of becoming sick. And also remember, eating a balanced diet doesn’t mean you will not ever fall sick. Although even if our immune system is working properly, it’s not unusual to have a cold, fever, or diarrhea sometimes. With that being clarified, let’s explore 7 types of food that play an important role in maintaining your immune system in the next section.
7 types of food for a healthy immune system
Here are the food types that support and maintain the immune system.
- Protein-Rich Food
All the immune cells and organs are made of protein. Without proper intake of protein, your immune system and overall well-being are reduced. Egg, chicken, beans, lentils, and dairy are common protein-rich foods that can support immunity.
- Vitamin C Rich Food
Vitamin C is one of the most crucial vitamins for a better immune system. They increase the movement of phagocytes, improve skin function, and also work as antioxidants. Citrus fruits, berries, guava, bell peppers, and kiwi are some of the richest sources of vitamin C.
- Vitamin A Rich Food
Vitamin A-rich foods help maintain healthy skin, which protects the body from pathogens. Pumpkin, spinach, sweet potato, carrots, and pumpkins are some of the great sources of vitamin A.
- Vitamin D foods
Vitamin D regulates T cells and helps balance the immune response. Fatty fish, egg, milk, and proper sunlight are essential for vitamin D.
- Zinc and Selenium Foods
Zinc and selenium foods help T-cell development and antibody production. They also support the immune system with antioxidant activity. Nuts, seeds, whole grains, and seafood contain a good amount of zinc and selenium.
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids
Omega-3s help control inflammation, support skin health, and improve cell communication. Fish, flaxseeds, and walnuts are a great source of natural antioxidants.
- Probiotic and prebiotic foods
Probiotic and prebiotic foods are essential for a healthy gut. The gut trains and strengthens the immune system. Yogurt, kefir, fermented food, oats and bananas, and garlic are some of the probiotic and prebiotic foods.

Immune Boosting Foods In A Balanced Diet
How does a balanced diet support immune system health?
A balanced diet means a diet that provides you with all the nutrition and energy that your body requires. A healthy diet is vital for a sound immune system. Lacking vitamins and minerals in your diet can weaken the function of your immune system in many ways. The immune cells decrease, and their function is also reduced. In this age of industrialization and a fast-paced lifestyle, it’s not hard to lose track of a healthy diet. High sugar, high fat, processed foods can interrupt your immune system further. They can also cause oxidative stress and inflammation in the body. By focusing on a healthy diet rich in vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, you can maintain a healthy immune system that protects you from infection and disease. Vegetables, fruits, fish, meat, eggs, whole grains, nuts, and seeds ensure your body gets all the essential nutrients you need to have a strong and resilient immune system.
Check out Healthy Diet: Benefits, Tips, and Mindful Nutrient Needs.
What foods should you avoid to protect your immune system?
You might wonder how many types of regular food can be harmful to immunity. Check them out,
- Sugary food: Food made with simple sugar causes inflammation and can reduce your immune system. They slow down the immune cells and make it harder for the body to fight infection. Always try to avoid high sugar foods like sodas, candies, and baked food items.
- Processed food: A lot of processed food contains unhealthy fat, artificial additives, preservatives, and high salt. Those can cause inflammation in the body and interrupt the immune system.
- Simple carbohydrates: Nowadays, everything is made of simple carbohydrates. Those carbs increase blood sugar very quickly, causing inflammation in the body. There is a reason simple carbs are very popular. They provide energy instantly and make you feel good just after you eat them. Due to their addictive nature, all industries use them in their products. But in the long term, they can disrupt the regular immune system.
- Excessive alcohol: Too much alcohol can damage the gut lining, cause inflammation, and stress the liver. Those can impair the immune system.
- High salt: High sodium foods can cause inflammation in the body, reducing the efficiency of the immune system.
- Too much caffeine: Coffee can disturb your sleep schedule and potentially reduce the efficiency of your immune system. It occurs due to lack of sleep not from caffeine.
How does sugar or processed food impact immunity?
Nowadays, we see a mass awareness against sugar. Some of you may feel Is sugar that bad? Yes, it’s quite bad as a habit. Let me tell you why in a minute. Sugar is addictive, and it’s everywhere. Most of the processed food these days contains sugar. There is an opposite revolution of non-sugar food out there, capitalizing on the risks of sugar. It might be very confusing sometimes. Let me start with the processed sweet food and its impact on immunity.
- Sugar intake directly impacts the immune cells. They slow down the white blood cells, reducing their ability to move and fight infection. If you consume simple sugar regularly, your immune system may be working in a reduced state.
- Simple carbohydrates and sugar can cause inflammation in the body with the same function. They increase the blood sugar instantly and drop it again very quickly. This can cause inflammation in the body, creating a risk of chronic disease in the long term and also reducing immunity.
- A huge part of our immunity depends on the health of our gut. Processed food and sugar are notorious for disrupting the gut environment and gut lining. A diet full of sugar and processed food can reduce the number and diversity of gut bacteria, leading to poor health and immunity.
- Processed food usually lacks antioxidants, leading to oxidative stress in the body. Free radicals damage the function of immune cells, causing health risks. Sugary food can also interrupt cell signaling.
- Fatty and sugary foods are high in calories and can easily cause obesity. Obesity causes chronic inflammation, reducing the immune function.
Can whole foods provide enough immune-supporting nutrients?
Yes, eating diverse whole foods is enough to provide you with immune-supporting nutrients. Whole grains, vegetables, fruits, meat, fish, nuts, and seeds contain all the essential nutrients you need for maintaining a proper immune system. On the other hand, processed foods often consist of one or a few types of food and additives, making you prone to nutrient deficiency and a poor immune system.
What lifestyle factors, alongside diet, support immune function?
Sleep, stress, hydration, physical exercise, happiness, and different addictions are some of the factors that directly impact your immune system. Deep sleep is a period of critical immune regulation and memory consolidation. Stress and happiness can also impact your inner metabolism, including the efficiency of the immune system. So meditation, mindfulness, and hobbies are equally important. Exercise also helps to release the happy hormone and directly improves immunity. Over Caffeine and nicotine addiction can cause inflammation and reduce the efficiency of the immune system.
How do exercise and hydration contribute to immune health?
Exercise is a free boost to your immune system and overall metabolism. It increases blood circulation, allowing the immune cells to travel faster and become more active. Exercise can also improve the production of immune cells. It improves the inflammatory reducing response in the body. Even moderate free-hand exercise can improve the antibody response in your body.
In every metabolic function of our body, water is a vital component. Proper hydration ensures the blood cells have enough fluid to function effectively. The body’s fluid balance is important for cell communication and immune response. Water also helps remove toxins, keep the mucosal membrane healthy, and maintain proper function of the lymphatic system.
Why is sleep important for the immune system’s performance?
Sleep is a crucial factor for a healthy immune system. During sleep, our body releases cytokines. Cytokines are the components that promote the activity of the immune system. With the presence of cytokines, B and T immune cells can work more effectively. Lack of sleep can lower the activity of those cells and make you more prone to disease. Sleep also increases the production of antibodies. Antibodies are proteins that are important for destroying pathogens. Without proper sleep, this function may not work optimally. Lack of sleep increases cortisol in our bodies. It’s the hormone that makes us feel tired. With its presence, the immune system is suppressed. So, as you can see, sleep has a direct connection to how your immune system will function.
How does immune-focused eating align with disease prevention?
Ideally, you don’t need to focus on the immune system if you have a balanced diet. Consuming vegetables, fruits, whole grains, animal, and plant protein foods has enough nutrients to maintain your immune system without ever worrying about them. But if you lead an unhealthy lifestyle for a long time, and can’t maintain a proper diet, you should focus on an immune boost diet. People with a poor immune system also need to focus on immune-boosting food. The simple reason – Poor immunity means high risk of disease. Your immune focus diet directly improves immune power and lowers the risk of severe disease.
If you are reading till now, you should have a good idea of whether you should eat and what to avoid.

What are the natural supplements for the immune system?
Vitamin C, Vitamin D, and Zinc are some of the top nutrients for the immune system. Supplementing those can fill the gaps of those nutrients supporting your immunity. Echinacea, elderberry, astragalus, omega-3, garlic, and turmeric are some of the natural supplements with powerful immune-supporting effects.
Vitamin C: Supports the production of immune cells, works as an antioxidant and improves immune activity.
Vitamin D: Enhances pathogen pathogen-fighting efficiency of immune cells.
Zinc: Required for the proper function of T cells.
Echinacea: Improves the production of white blood cells.
Elderberry: Contains anthocyanins and immune-boosting nutrients.
Astragalus: Improves immune response and production of immune cells.
Omega-3: Reduce inflammation and support immune cell formation.
Garlic: Comes with an antimicrobial component and gut health-boosting effect.
Turmeric – Curcumin from turmeric helps to improve the immune system.
Please read Superfoods for wellness : An Honest Guide for Beginners.
Are supplements really important to boost your immunity?
Those supplements are not required for everyone. If you are having a blanched diet with enough greens, protein, and whole foods, you get all the nutrients you need for proper immunity. The rest are dependent on other factors like exercise, stress, sleep, etc. But if you have poor immunity and get sick easily, immunity supplements can help you in the process. The natural supplements help boost immunity.
Final Thoughts
The immune system is the invisible protector of our body. It’s so complicated and powerful that we never have to worry about it. And that also makes it easy to completely ignore the wellness of your immune system. Questions like “Why am I always sick and weak?”, when all you are eating is processed food, cans of soda, and very little vegetables. This is one of the problems of modern fast-paced life, where most people have no clue about their wellness and diet.
We cover a lot of ground on the immune system and healthy foods with lifestyle to create awareness. This will give you a better idea of the immune system & wellness.
Please read the best supplements for the immune system.
Mr. Shariful Alam Pavel believes in natural living. To live a healthy conscious living, we need to eat green, live green. MyOrganic Bd is a green wellbeing brand, educating millions to live a better life with mother nature.
- Shariful Alam
- Shariful Alam
- Shariful Alam
- Shariful Alam
- Shariful Alam
- Shariful Alam
- Shariful Alam
- Shariful Alam
- Shariful Alam
- Shariful Alam
- Shariful Alam
- Shariful Alam
- Shariful Alam
- Shariful Alam
- Shariful Alam
- Shariful Alam
- Shariful Alam
- Shariful Alam
- Shariful Alam
- Shariful Alam
- Shariful Alam
- Shariful Alam
- Shariful Alam
- Shariful Alam
- Shariful Alam
- Shariful Alam
- Shariful Alam
- Shariful Alam
- Shariful Alam
- Shariful Alam
- Shariful Alam
- Shariful Alam
- Shariful Alam
- Shariful Alam
- Shariful Alam
- Shariful Alam
- Shariful Alam
- Shariful Alam
- Shariful Alam
- Shariful Alam
- Shariful Alam
- Shariful Alam
- Shariful Alam
- Shariful Alam
- Shariful Alam
- Shariful Alam
- Shariful Alam
- Shariful Alam
- Shariful Alam
- Shariful Alam
- Shariful Alam
- Shariful Alam
- Shariful Alam
- Shariful Alam
- Shariful Alam
- Shariful Alam
- Shariful Alam
- Shariful Alam
- Shariful Alam
- Shariful Alam
- Shariful Alam
- Shariful Alam
- Shariful Alam
- Shariful Alam
- Shariful Alam
- Shariful Alam
- Shariful Alam
- Shariful Alam
- Shariful Alam
- Shariful Alam
- Shariful Alam
Dr. Goutom Banik, MBBS, MPH, is a public health researcher with extensive experience in maternal, newborn, and child health, including nutrition interventions in underserved communities. He has worked with leading organizations such as Save the Children and icddrb, contributing to national strategies on child health and nutrition. His expertise spans operational research, health systems strengthening, and community-based programs addressing childhood illness.
- Dr Goutom
- Dr Goutom